Project Report Preparation Guide for 15 Cows Farm
We always strive to make enough profits from our dairy business for which we need to arrange good feed, fodder, and management. The cows have productive life hence replacement is necessary which can be done either by rearing their own heifers or purchasing from outside. For establishment or for expanding the farm, many a time bank loans are unavoidable. Since under the government schemes soft interest loans are available, the farmers are advised to take benefit of such schemes rather than spending from their profits. For starting a new dairy business or expansion, it is important to prepare a dairy farm project report.
How to prepare Dairy Farm Project Report is a question farmers frequently ask? I describe a project report template for 15 animals.
While finalizing the project, please keep the following important points in your mind. These are extremely critical to your long-term profits.
- Self-involvement – You should be ready to invest your time in monitoring and management.
- Housing: This is critical. The housing should be for the comfort of the cow, hence ask the veterinarian.
- Low Cost but Good for Cow: Do not spend excessively on cow housing, as the more you spend closing the business due to unavoidable reasons becomes difficult and loss-inflicting.
- Small farmers should use the local material available for housing
- Insist on not tying the animals, they should be kept loose all the time.
- Invest in a better quality floor, preferably an earthen floor, so that the house is dry all the time and there is no need to wash the animals and the floor.
- Consider how and where you will dispose of the manure as it is related to your family’s health as well as cow health.
- Since in India, cows can’t be culled hence better option is go-to for medium yield cows that will last longer and give you more lactations rather than very high-yielding cows but have a short productive life.
Know the bank rules, interest rates, and the duration of repayment. Do not hesitate to ask if there are any hidden charges. These are the things you need for a project report and if you report the project accordingly, the bank will accept such a complete report, otherwise sending it back for correction may cause unnecessary inconvenience to the animal keeper. And these children may be late in disbursing loans.
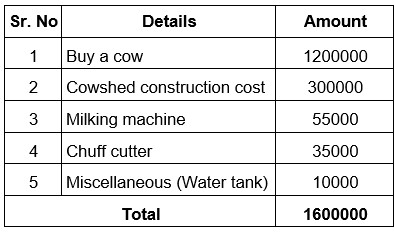
Initial Expenses: – This includes the capital expenditure that we have, such as the purchase of cows, the cost of raising the cowshed as well as the equipment required for it. The bank gives you a loan based on this amount.
Capital costs
- Purchase of Animals: – In this, you have to mention the amount required for the purchase of animals. This price is determined by NABARD according to the type and breed of the animal and the prices vary according to the market price. This includes the original cost of the animal and insurance. If you want to buy animals over long distances, it is also beneficial for the animal keeper to take out travel insurance. Consult a veterinarian to certify health and the breeding status. Do not compromise on the quality and health of the cow.
- Shed erection cost: – This includes the cost of erecting the cowshed. One thing to keep in mind is that you are doing this business by taking out a loan and you want to repay the loan, so you should reduce the cost to the place where you can spend the least. Because when we run our business at a good profit, we can spend a lot on such things. Because this time the money you have is yours and you don’t have to pay interest for it.
At such times we can plan our barn with foresight. In addition to the cost of the shed, you need to consider the shed to store the equipment you need to meet the basic needs of your shed.
- In this project report, we can mention different things like a threshing machine, milking machine, drying utensils, silage system, fodder transport system, fodder storage space, fodder storage space according to the number of our animals in the financial planning project report.
- Other Expenses: – Includes electricity supply and related costs, water supply, and storage costs as well as some other small expenses
Technical part
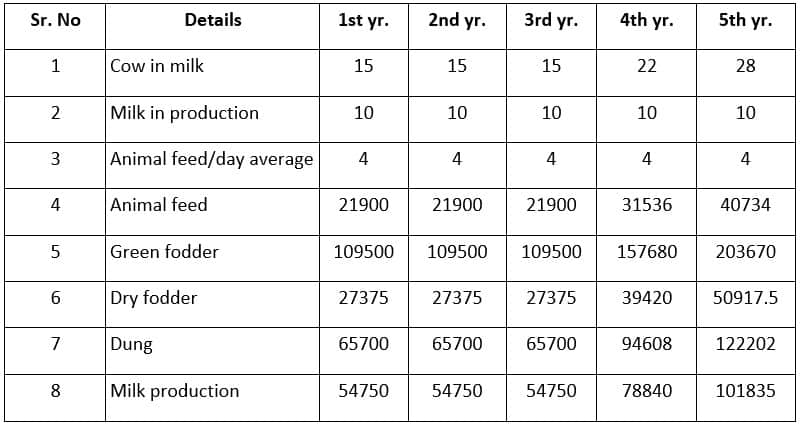
When you are preparing this project report, you are thinking about your animal’s diet, health, milk production, breeding, and dung production.
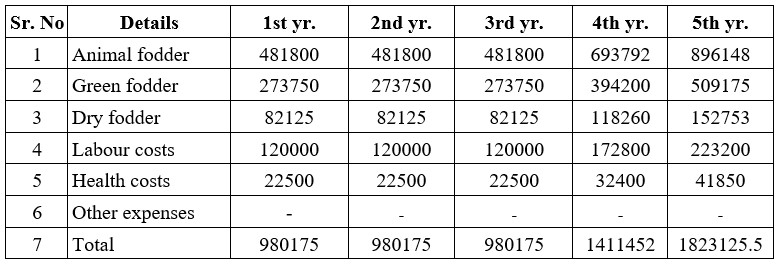
- Feed Cost; – It mentions how much-wet fodder, dry fodder, animal feed, and other food supplements your animals will need for 1 year considering their normal gestation period, milk production, and calving period for the next 5 years.
- Health Expenses: – This includes the cost of timely vaccination, deworming, medication, and other health care for your animals for the next 5 years.
- The first milking age of calves in this project is generally 2.5 years. The cost of calves is assumed to be 60% of the total management cost up to this age and according to market valuation, their per calf income is 35,000.
- The cows that we are going to raise will probably be in the first or second calf so that they will stay in your barn longer. Their market value is currently Rs. 80,000 is taken out with insurance.
- The milking capacity of a cow is how much milk a cow gives in one calf and the distance between two calves of a cow determines how much milk is given in a year. In this place, the interval between two calves is generally considered to be one to one and a half years and the average milk production is considered to be 10 liters per day.
- The price of milk is Rs. 30 per liter, green fodder Rs. 2.5 per kg, dry fodder Rs. 3.00 per kg of dung Rs. Rates are considered as 2.00 kg. It would be appropriate to decide the rate considering your situation.
Total cost
Actual Expenditure: – If we mention the capital expenditure above, this second section includes how much it costs to run the actual herd throughout the year. This includes fodder, animal feed, labor costs, health costs as well as depreciation costs. This cost planning is for the next 5 years.
Income
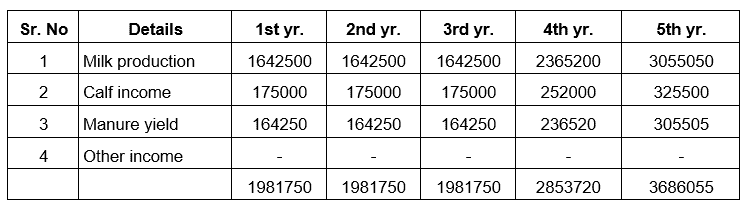
Milk: – The price of milk a farmer receives although relatively constant is never adjusted for the cost of production. The procurement cost is decided by the processor but the feed and other costs are highly volatile. A better option is to look for your own market, rather than giving it to a milk processor.
- Calf rearing: – In fact rearing calves for replacement and excess calves for sales would add to maybe income equal to what you get from milk. The calf should be of high pedigree and you should maintain pedigree records. Selling excess pregnant heifers is a good supplementary activity to milk production. The calf is usually ready to give milk in two and a half years. The price is for two and a half years. If you divide it by 2/5, you can find out how much income you get from your calf in one year.
- Manure: – After this, the second source of income is manure which does not get much attention from the animal keepers. This includes the production of different types of quality fertilizers. We can increase the price of cow dung by ten times. These include bokashi, jivamrit, organic manure, ghanamrit. And we can increase the income of our dairy business by producing many such quality fertilizers. A good cow usually gives 12-18 kg of dung in a day. The value of dung is calculated according to the market price
Other income: – We can include other sources of income in our dairy business. Selling animal feed bags e. The kind of income we can take into it.
Debt repayment
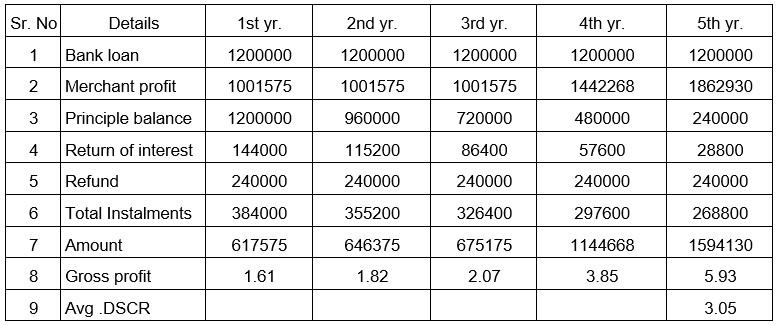
This is mostly a matter of the bank and the amount of margin money controlled by the bank is often 10 to 25%. It is also important to consider the interest rate of the bank. This table gives you information on how much you will get in installments, interest, and the bank’s principal interest, and how much profit you have leftover per year. The bank decides whether to lend to you based on the cost, investment, and profit.
You may like to read: Dry Matter Requirements for Dairy Cows
Assistant General Manager Dairy Development Department
Govind Milk, Phaltan, Dist. Satara