Prevention and Treatment of Foot and Mouth Disease
Foot and mouth disease is a severe, highly contagious viral disease of cattle and swine. It also affects sheep, goats, deer and other cloved-hooved ruminants. It is a disease that causes a significant economic impact.
Etiology: Causitive agent: Apthovirus, of the family Picornaviridae. Presently 7 immunological and serological main types and 60 sub types have been identified. There are 7 strains (A, O, C, SAT 1, SAT 2, SAT 3 and Asia 1) In Maharashtra O, A, C and Asia 1 are main types and A-22 subtype were found. It is the smallest of all the viruses and has affinity towards epithelial tissue of mouth and foot.
Animals succeptible: Cattle, buffeloes, sheep, goats.& pigs. Wild animals like neelgai, yak, antelopes and deer. Exotic and crossbred animals are more succeptible. Young animals found more succeptible to the disease.
Transmission: By inhalation & injestion. Virus excreted through all secretion & excretions. Spread by infected pasture & personnel. Air borne virus spread depend on speed of air temperature & humidity. Drizzling rains enables deposition of virus on the earth & sheds.
Incubation period: 1-7 days
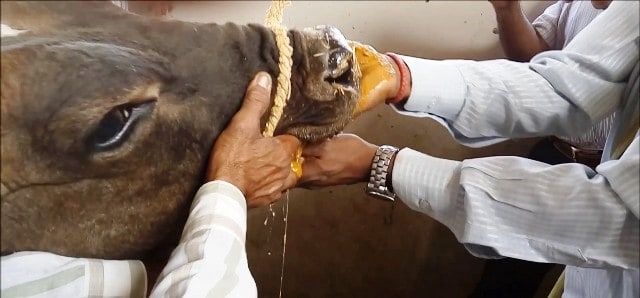
Clinical symptoms: Cattle-Hyperpyrexia, anorexia, acute stomatitis & profuse long, ropy salivation,blister likesores on the toung and lipd, smacking of jaws, careful chewing, vesiculation on buccal mucosa, dental pad & tongue. Vesicals in interdigital space, coronate band, vesicles seen also on the udder and teats. Drop in milk yield, sudden death in sucking young calves, kids and lambs.
Sheep & goats- oral lesions usually mild lesions mainly on the feet.
Pigs- oral lesions mild, prominent lesions on the feet and snout. Marked lameness, heavy mortality in suckling pigs due to severe gastro enteritis & myocarditis.
Complications and sequeliae – Abortion due to hyperthermia & subsequent infertility. Rapid loss in the condition. Rupture of vesicles in the digital cleft leading to acute lameness and discomfort. Secondary bacterial and parasitic infestations. Deformities of hooves. Vesicle on teat, leading to mastitis, rough bodycoat, dyspnoea, anaemia, heat-intolerance, panting syndrome.
Postmortem Lesions: Cattle- Lesions on trachea and larynx. Heart filled with blood due to myocarditis.
Calves: “Tigrroid heart”.
Mortality in young lambs due to myocarditis and skeletal muscle necrosis.
Suckling pigs – severe gastroenteritis and myocarditis
Differential diagnosis: Swine vesicular disease, vesicular stomatitis, contagious ecthyma in sheep and goats, sheep and goat pox, blue tongue in sheep, Rinderpest.
Diagnostic Tests: Complement Fixation Test, (C. F. T.) Biological Test, ELISA, PCR.
Treatment:
- Wash mouth lesions with mild lotions viz. 1 % – 2 % Alum lotion, 4 % sodium carbonate solution and apply boroglycerine 2-3 times in a day.
- Wash foot lesions with disinfectant solution viz. savlon.
- Dettol and dress the wound with boric acid or Zinc oxide ointment.
- Broad spectrum antibiotics to avoid secondary bacterial infections.
- 5% dextrose with Ringers Lactate or Physiological saline.
- Sequellae symptoms to be treated symptomatically.
Prevention: Timely vaccination as per instructions of manufacturers.
| Dr. V. M. Bhuktar
Former I/c Joint Commissioner of A.H, D, I, S. Government of Maharashtra, Former Chairman disciplinary committee VCI New Delhi.
|
Dr. K. R. Shingal
Former Regional Joint Commissioner of Animal Husbandry, |
